AI agents have become one of the most popular topics of conversation today, particularly among early adopters and AI enthusiasts. Many businesses across various industries are trying to understand how to implement AI agents in their operations, while many are already testing or using them. Following AI and ML trends, we became curious about the capabilities of agentic AI to transform decision-making, automate workflows, and enhance user experiences. And why Forbes calls 2025 the year of Agent AI. So let’s find out what’s in it.
What are AI Agents?
AI agents are software programs that operate either autonomously or semi-autonomously. They effectively understand the environment where they operate, analyze data, make informed decisions, and take decisive actions to achieve specific goals
Before making any business decision, it’s crucial to assess the value of the technology being considered. This means understanding its core functionality, capabilities, and potential impact.
Today, we’re focusing on AI agents – exploring how they work and the potential benefits they bring to businesses. We’ve already started uncovering their essence, so let’s dive deeper into the subject.
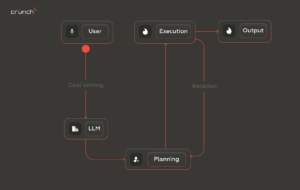
How do AI Agents work?
AI agents function through a combination of software, algorithms, and hardware components. The technologies that empower their effective operation involve:
Machine Learning & Deep Learning
ML/DL models help process data, recognize patterns, and improve decision-making. Common frameworks include TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn.
Natural Language Processing
AI agents utilize NLP models such as GPT and BERT for effective communication and understanding of human language.
Sensors
Some AI agents interact with the physical world using sensors, including:
- cameras (used in autonomous vehicles and robotics for object detection and navigation)
- temperature and motion sensors (common in smart home assistants and industrial automation)
- microphones and speech recognition (enable voice assistants like Siri and Google Assistant to understand and respond to commands)
Computer Vision
AI agents utilize image recognition and video analysis to understand their environment. Key technologies: OpenCV, YOLO, and CNNs.
Cloud Computing
Cloud platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure offer the necessary computational power to run AI models.
However, the choice of technology depends on the type of AI agent required for the specific case, so the next step is to determine which type of AI agent best fits the intended application.
What are the Types of AI Agents? What Can AI Agents Do?
The information about the types of AI agents and their quantity varies by source, but we will cover all the known ones at this time:
1. Simple reflex agents
It operates solely based on predefined rules and the immediate data it receives. These agents are suitable for simple tasks that do not require extensive training: sorting incoming emails into predefined categories based on detected keywords.
2. Model-based reflex agents
A model-based agent evaluates possible outcomes and their implications before making a choice, instead of simply following rigid rules. In a smart thermostat, such a system might analyze factors like current temperature, weather forecasts, and user preferences to predict the optimal temperature settings for the home, rather than just responding to a simple command.
3. Goal-based agents
These agents compare various strategies to determine the best way to achieve their desired outcomes. They are particularly well-suited for performing complex tasks, including natural language processing (NLP) and robotics applications. For instance, in a customer support chatbot, such an AI agent might compare various response strategies to provide the most accurate and helpful answer to a user’s query, considering past interactions, user sentiment, and contextual data to craft the best response.
4. Utility-based agents
The utility-based agent is primarily concerned with optimizing outcomes based on a predefined set of preferences or values, ensuring the highest benefit for the user. It can help users find the most convenient delivery options, prioritizing faster delivery times over cost, and ensuring they receive their package as quickly as possible, regardless of the price.
5. Learning agents
A learning agent distinguishes itself by continuously improving its performance over time. Unlike the other agents, which follow predefined rules, models, or utility functions, a learning agent actively learns from past experiences and adapts its strategies to achieve better outcomes in the future.
As an example, for an online streaming platform (Netflix or YouTube), a learning agent continuously learns from user behavior. It tracks which movies or shows a user watches, how much time they spend on them, and their ratings. Over time, the agent adapts its recommendations based on this accumulated data, improving its suggestions to align more closely with the user’s preferences.
6. Hierarchical agents
Hierarchical agents differ from the previously discussed ones in their structured decision-making process. They organize their actions in a multi-level system, where decisions are made at various layers of abstraction. Each layer is responsible for different tasks, which allows for more complex problem-solving and efficient handling of larger tasks.
For example, in a robotic vacuum cleaner, a hierarchical agent might first decide on the high-level goal (cleaning the entire house), and then delegate the task to lower-level agents responsible for specific rooms, paths, or obstacles. The higher-level agent might reassess the progress or goals, while the lower-level agents focus on navigating and cleaning. This layered structure allows the agent to effectively handle complex tasks without becoming overwhelmed by individual details.
7. Collaborative agents
Collaborative agents are capable of coordinating, communicating, and sharing information to improve overall performance, solve problems, or complete tasks that would be difficult for a single agent to handle alone. In a smart home system, collaborative agents work together to optimize comfort and energy efficiency. One agent monitors temperature, while another controls lighting based on occupancy. If a room is unoccupied, the temperature agent notifies the lighting agent to dim the lights, saving energy and ensuring seamless operation.
AI Agents vs. Advanced Automation – What’s the Difference?
Not all AI systems qualify as true AI agents. While automation tools can enhance workflows and support decision-making, genuine AI agents must function “a little” differently. How can you distinguish between them?
- Autonomy – an AI agent acts independently rather than relying on pre-programmed rules.
- Learning ability – AI agents adapt based on feedback, while automation tools follow fixed processes.
- Goal-oriented behavior – AI agents dynamically adjust their strategies to achieve goals instead of executing rigid scripts.
- Resilience – AI agents continue functioning even when unexpected variables arise, whereas automation tools often require human intervention when things don’t go as planned.
To make it easier to understand which system you are working with, you can complete a small quiz:
- Does the system require constant human input to function?
- A) No, it operates independently and takes action on its own.
- B) Yes, it follows predefined rules and needs human approval.
- Can the system adapt based on feedback and improve over time?
- A) Yes, it learns from past actions and evolves.
- B) No, it sticks to its initial programming.
- Does it have dynamic goal setting, adjusting its approach as needed?
- A) Yes, it shifts strategies based on real-time data.
- B) No, it executes fixed workflows without adjusting.
- What happens if the environment changes unexpectedly?
- A) The system recognizes the issue and adjusts its behavior.
- B) It gets stuck or fails without intervention.
- Does it make decisions based on reasoning and data analysis?
- A) Yes, it analyzes data and determines the best course of action.
- B) No, it simply executes predefined steps.
Results:
Mostly A’s? You’re working with a real AI agent!
Mostly B’s? It’s an automation tool, not a fully autonomous AI agent.Benefits of Using AI Agents
Depending on the sector, that employs AI agents, and the kind of technology, there are many benefits it can provide, but if we combine, we will obtain the following list:
Automation of repetitive tasks
AI agents reduce human effort by doing repetitive tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and customer queries, freeing up employees to do more worthwhile work.
Better decision-making
Through the analysis of large amounts of data in real time, AI agents offer suggestions and feedback that enable companies to make smarter and more informed decisions.
Improved customer experience
AI-powered chatbots, personalized recommendations, and automated support systems all help achieve faster response times and a more personalized user experience.
Cost reduction
Automation of processes reduces the cost of labor and operational costs, leading to tremendous savings across sectors, ranging from manufacturing to customer service.
Scalability
Companies can expand their operations without requiring proportional human resource expansions since AI agents can process high levels of tasks in parallel.
Real-time data processing
AI agents examine and act upon information in real-time and are thus appropriately utilized for applications like fraud detection, supply chain management, and predictive maintenance.
Flexibility
Learning agents constantly get better with machine learning and adapt to new situations, thereby growing more efficient over time.
What is an AI agent in real-life examples?
In this article, we’ve covered the industries that implement AI agents faster than others because they rely on big data and have high automation potential. To be short, this list includes such industries: IT & software development, finance, retail/e-commerce, supply chain & logistics, and telecommunications. Now, let’s examine some real-world examples of AI agents.
GitHub Copilot
AI-powered coding assistants like GitHub Copilot use ML and NLP to enhance developers’ coding efficiency and speed. It suggests entire lines or functions, reducing repetitive tasks and improving productivity, by analyzing the context of a developer’s code.
AI fraud detection by Mastercard
Financial institutions leverage AI agents mostly for fraud detection and risk assessment: Mastercard, for instance, employs AI-driven systems that monitor real-time transaction patterns. If unusual spending behavior is detected, the AI agent immediately flags or blocks the transaction, reducing fraud risks and minimizing false positives.
Amazon’s personalized recommendations
E-commerce platforms like Amazon use utility-based AI agents to analyze user preferences, browsing history, and past purchases. These agents help generate personalized product recommendations, optimizing sales, and enhancing the customer experience.
FedEx route optimization
Logistics companies such as FedEx employ AI-powered route optimization agents to streamline deliveries. These agents evaluate real-time traffic data, weather conditions, and package volume to recommend the most efficient delivery routes, minimizing delays and fuel consumption.
AI Chatbots for customer support
Telecom giants such as AT&T and Verizon utilize AI chatbots to manage customer inquiries, troubleshoot technical issues, and process service requests. These AI agents enhance customer service efficiency by resolving common problems without human intervention, which enables humans to concentrate on more complex cases.
At Crunch.is, we can develop and implement AI-driven solutions tailored to your specific business needs. Our AI Proof of Concept (PoC)approach guarantees that your AI-driven solution is thoroughly tested, optimized, and aligned with your business goals before full-scale deployment. Whether it’s enhancing fraud detection in financial services, personalizing customer interactions in telecom, or predicting demand in retail, our team of AI experts is here to assist you.
These instances show how AI agents are transforming industries by enabling things to be more efficient, easier to use, and automated. As AI technology evolves, we can expect even more sophisticated agents capable of performing even more complex tasks in a variety of areas. The future of AI agents lies in becoming adaptable, learnable, and collaborative, paving the way for smarter, more intuitive automation.
Conclusion
AI agents are transforming industries through process automation, decision-making AI agents are revolutionizing industries by automating processes, enhancing decision-making, and enriching customer relationships. AI have a distinct competitive advantage whether it’s optimizing operations in IT or streamlining logistics, businesses leveraging.
Are you ready to unlock the transformative power of AI for your business? Contact us today and discover how AI agents can propel your organization to new heights!
- Does the system require constant human input to function?


![How Much Does It Cost to Build AI Solutions In 2025 [Ultimate Guide]](https://crunch.is/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/steve-johnson-1FD-E7Ioblw-unsplash-scaled.jpg)